Roofing terms you should know
Deck/Sheathing: The surface, usually plywood or oriented strand board (OSB), to which roofing materials are applied.
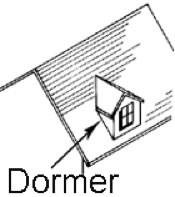
Dormer: A small structure projecting from a sloped roof, usually with a window.
Drip Edge: An L-shaped strip (usually metal) installed along roof edges to allow water runoff to drip clear of the deck, eaves and siding.
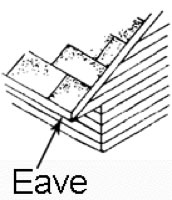
Eave: The horizontal lower edge of a sloped roof.
Fascia: A flat board, band or face located at a cornice’s outer edge.
Felt/Underlayment: A sheet of asphalt-saturated material (often called tar paper) used as a secondary layer of protection for the roof deck. Underlayment is also available in synthetic materials.
Fire Rating: System for classifying the fire resistances of various materials. Roofing materials are rated Class A, B or C, with Class A materials having the highest resistance to fire originating outside the structure.
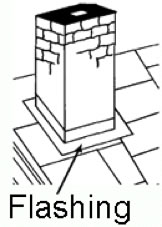
Flashing: Pieces of metal used to prevent the seepage of water around any intersection or projection in a roof system, such as vent pipes, chimneys, valleys and joints at vertical walls.
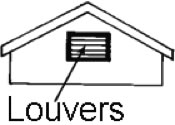
Louvers: Slatted devices installed in a gable or soffit (the underside of eaves) to ventilate the space below a roof deck and equalize air temperature and moisture.
Oriented Strand Board (OSB): Roof deck panels (4 by 8 feet) made of narrow bits of wood, installed lengthwise and crosswise in layers, and held together with resin glue. OSB often is used as a substitute for plywood sheets.
Penetrations: Vents, pipes, stacks, chimneys-anything that penetrates a roof deck.
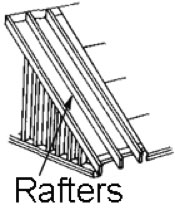
Rafters: The supporting framing to which a roof deck is attached.
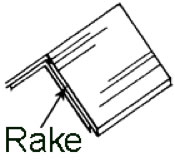
Rake: The inclined edge of a roof over a wall.
Ridge: The top edge of two intersecting sloping roof surfaces.
Sheathing: The boards or sheet materials that are fastened to rafters to cover a house or building.
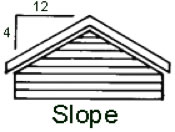
Slope: Measured by rise in inches for each 12 inches of horizontal run: A roof with a 4-in-12 slope rises 4 inches for every foot of horizontal distance.
Square: The common measurement for roof area. One square is 100 square feet (10 by 10 feet).
Truss: Engineered components that supplement rafters in many newer homes and buildings. Trusses are designed for specific applications and cannot be cut or altered.
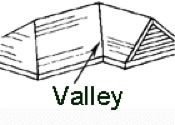
Valley: The angle formed at the intersection of two sloping roof surfaces.
Vapor retarder: A material designed to restrict the passage of water vapor through a roof system or wall.
To go directly to what you are most interested in, please click below.
– Choosing the Right Roof Covering
– Roofing Terms You Should Know
– Protect Your Roof From Its Enemies
– FAQs
Residential Roofing
Residential Roofing
A residential building is one in which people live. To be considered residential in the state of Virginia the building must contain no more than 4 private living spaces.
Commercial Roofing
Commercial Roofing
A commercial building is used for the purpose of conducting business. This may include a multi-family residential structure as well. Some examples include buildings used for retail, office, warehouse, churches, and apartment complexes.
Industrial Roofing
Industrial Roofing
An industrial building is used to manufacture consumable goods. Churches may also be classified as industrial structures.
Rapid Rain Gutter Systems
Rapid Rain Gutter Systems
The key to the Rapid Rain Gutter System’s uniqueness is the AR5600 Technology that provides a large capacity system that doesn’t look large or bulky, but achieves high-volume control of water flow.
Our Brands
Website built & maintained by Bull & Company MediaWorks





